Demystifying Insurance Premiums: What You're Really Paying For

An insurance premium is the regular payment you make to an insurance company to maintain active coverage. Think of it as your subscription to financial protection. These payments are the foundation of the insurance system, allowing insurers to pool resources from multiple policyholders and pay out claims when necessary. This core principle of risk-sharing is the engine that drives the entire insurance industry.
Understanding Your Premium vs. Other Costs
It's important to distinguish your insurance premium from other associated costs. A deductible, for instance, is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage takes effect. A copay, on the other hand, is a fixed fee you pay for a specific service, such as a doctor's visit. In short, your premium keeps your policy active, while your deductible and copay represent cost-sharing when you utilize your insurance benefits.
This agreement between you and the insurer hinges on your premium payments. By paying your premium, you uphold your end of the contractual obligation. In turn, the insurer is obligated to provide the coverage specified in your policy. Failure to pay your premiums breaches this agreement, potentially leading to policy termination.
The Rising Cost of Premiums
The cost of insurance premiums is not fixed. It's subject to change, often influenced by market forces and economic conditions. Over the past five years, premiums have seen an average annual increase of 8 percent. This upward trend is attributable to several factors, including rising claims costs and insurers implementing rate hikes to maintain profitability across various property and casualty (P&C) insurance lines. For a deeper dive into these statistics, visit McKinsey's Global Insurance Report. Understanding these trends helps put your own premium costs into perspective.
Different Types of Insurance, Different Premiums
Premiums vary considerably depending on the specific type of insurance. For example, your car insurance premium is calculated differently than your health insurance premium. Each policy type considers a unique set of factors to assess your risk level, ultimately determining your premium amount. For homeowners specifically, you might find Demystifying Homeowners Insurance: Understanding Your Coverage helpful. Truly understanding your insurance costs requires not just knowing the definition of a premium, but also grasping how your specific type of insurance evaluates risk and sets pricing.
The Science Behind Your Premium Calculation

Have you ever stopped to consider how insurance companies arrive at your premium? It isn't a random number; it's the result of a detailed process designed to assess your level of risk. This process utilizes complex algorithms and risk assessment models to create personalized rates. Understanding this process can empower you to make more informed decisions when selecting insurance coverage.
Understanding how your premium is calculated can also help you compare different policies and providers more effectively.
Understanding Risk Assessment
Insurance companies gather and analyze data to predict the likelihood of you filing a claim. This prediction is based on several factors, ultimately generating a unique pricing profile for every individual. This means your insurance premium is specifically tailored to your individual circumstances.
For example, a younger driver with a history of speeding tickets will likely pay a higher auto insurance premium than an older driver with a clean record. This is because statistically, younger drivers with speeding violations are more likely to be involved in accidents.
Factors Influencing Your Premium
Several key factors contribute to your insurance premium calculation. These factors are typically categorized into personal information, property characteristics, and coverage selections. Let's explore each category in more detail.
- Personal Information: This includes data points such as your age, location, and credit history. Younger individuals, for instance, often pay higher premiums for car insurance. Those living in areas with higher crime rates might also see increased premiums for homeowners insurance.
- Property Characteristics: For property insurance like homeowners or auto insurance, the specifics of the insured property play a significant role. The construction materials of your house or the safety features of your vehicle can influence your premiums. A house made of brick is generally more resistant to fire damage than a wooden house, potentially resulting in a lower premium.
- Coverage Selections: The amount of coverage you choose has a direct impact on your premium. Higher coverage limits usually result in higher premiums. Opting for additional coverage, such as flood insurance, will also increase your overall cost.
To illustrate these factors and their impact, let's examine the following table:
Key Factors That Influence Your Insurance Premiums
This table shows the primary factors that insurance companies consider when calculating premiums across different insurance types.
| Factor | Impact on Premium | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Younger individuals often pay more for certain types of insurance (e.g., auto, health) | A 20-year-old driver will likely pay a higher auto insurance premium than a 40-year-old driver. |
| Location | Living in high-risk areas (e.g., high crime rates, natural disaster zones) can increase premiums. | Homeowners in coastal areas may pay higher premiums due to the increased risk of hurricane damage. |
| Credit History | A poor credit history can often lead to higher insurance premiums. | Individuals with a history of late payments or defaults might experience higher premiums. |
| Property Characteristics | The features and condition of your property (e.g., home construction materials, vehicle safety features) can affect premiums. | Homes with fire alarms and burglar alarms often qualify for lower homeowners insurance premiums. |
| Coverage Selections | Choosing higher coverage amounts and optional add-ons increases premiums. | Adding comprehensive coverage to an auto insurance policy will increase the premium. |
This table provides a concise overview of some key factors that can influence your insurance premiums. Remember that each insurance company has its own specific underwriting guidelines.
How Underwriting Works
The process of evaluating your risk and determining your premium is called underwriting. Underwriters analyze the information you provide and leverage actuarial science to calculate your premium. Certain factors have a greater influence on your premium than others. For example, in auto insurance, your driving record typically has more of an impact than the color of your car.
Influencing Your Premium
While some factors are beyond your control, you can take steps to positively impact others. Maintaining a good credit score, choosing a car with advanced safety features, and opting for a higher deductible can all result in lower premiums. Understanding how these factors interact empowers you to make well-informed decisions about your insurance coverage and potentially save money. By understanding the science behind premium calculation, you can proactively manage your insurance costs.
Premium Variations Across Insurance Types: What To Expect
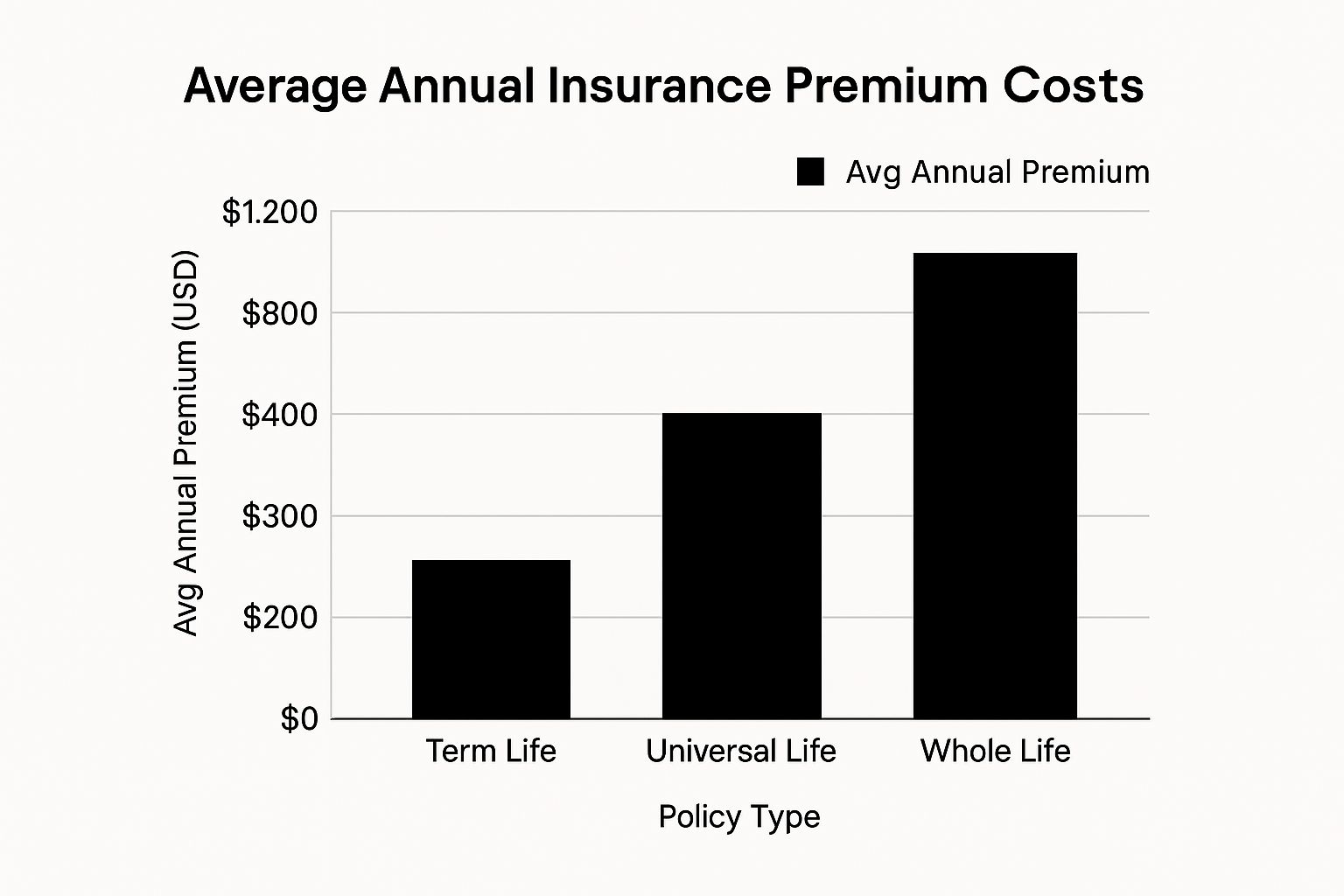
This data chart provides a visual representation of the average premium costs across various insurance types, categorized by coverage levels. As you can see, premium costs can vary significantly depending on the type of insurance and the level of coverage you choose.
Not all insurance premiums are created equal. Understanding what an insurance premium is within the context of different insurance types is crucial for making informed decisions. This section explores how premium structures vary significantly across major insurance categories, from life and health insurance to auto, home, and business coverage.
Life Insurance: Age and Health as Primary Factors
Life insurance premiums are heavily influenced by your age and health. Younger, healthier individuals generally secure lower premiums, reflecting a statistically lower risk.
For example, a 25-year-old in excellent health will pay significantly less for life insurance than a 60-year-old with pre-existing conditions. This is because the risk of death statistically increases with age.
Additionally, the type of life insurance policy—term life or whole life—also influences premiums. Whole life policies, offering lifelong coverage and a cash value component, typically have higher premiums than term life policies.
Health Insurance: A Complex Landscape
Health insurance premiums are often determined by factors like age, location, and the chosen plan. Pre-existing conditions can also significantly affect premiums in some markets.
Some health insurance plans, such as HMOs, might offer lower premiums but restrict your choice of doctors and hospitals. PPOs, conversely, offer more flexibility but often come with higher premiums.
Understanding these nuances is vital for choosing a health plan that balances cost and coverage.
Auto Insurance: Location, Driving Record, and Vehicle Type
Auto insurance premiums are calculated based on your driving record, location, the type of vehicle you drive, and your coverage choices. A clean driving record and a safe vehicle equipped with advanced safety features can often lead to lower premiums.
Location matters because areas with high rates of accidents or theft typically have higher auto insurance premiums. For more information on auto insurance companies, you can check out this resource: Stay Protected: The Best Car Insurance Companies of 2025 Revealed.
Home Insurance: Property Value, Location, and Coverage Amount
Home insurance premiums are largely determined by the value of your property, its location, and the coverage amount you select. Homes located in areas prone to natural disasters, such as floods or hurricanes, will typically have higher premiums.
The age and construction of your home also play a role, with older homes or those built with less fire-resistant materials potentially facing higher premiums.
Business Insurance: Industry, Risk Level, and Coverage Needs
Business insurance premiums vary widely depending on the industry, the specific risks associated with the business, and the coverage selected. A small business with minimal risk might pay a lower premium than a large corporation operating in a high-risk industry.
The type of business insurance needed also impacts premiums. For instance, professional liability insurance often costs more than general liability insurance.
Benchmarking Your Insurance Premiums
To better understand typical premium ranges, let's take a look at the table below:
Average Premium Costs By Insurance Type
| Insurance Type | Basic Coverage | Standard Coverage | Premium Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto | $1,500 | $2,000 | $2,500 |
| Homeowners | $1,200 | $1,600 | $2,000 |
| Health (Individual) | $5,000 | $6,500 | $8,000 |
| Life (Term – $500k) | $300 | $400 | $500 |
| Business | Varies widely | Varies widely | Varies widely |
This table provides a general overview of average premium costs. Remember, these are just averages, and your individual premiums may differ based on your specific circumstances. Business insurance, in particular, has a very broad range depending on the industry and coverage.
Market Trends in Insurance
Recent trends in the commercial insurance market show interesting shifts. Global commercial insurance rates decreased by 3% in the first quarter of 2025 after seven years of quarterly increases. However, this trend varies regionally. U.S. casualty rates actually increased by 8% due to high claim payouts and "nuclear verdicts". More detailed statistics can be found here. Understanding these market dynamics can help you better understand your own insurance premiums.
Market Forces Reshaping Your Insurance Costs
Your insurance premium, the cost of your coverage, isn't determined solely by your individual risk profile. Larger market forces significantly influence prices across the entire insurance landscape. These forces can shift unexpectedly, impacting what you pay. Understanding these dynamics can help you anticipate future premium changes and make informed decisions about your insurance needs.
Macroeconomic Factors and Insurance Premiums
Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and interest rates, directly impact insurance premiums. During periods of high inflation, the cost of everything rises, including medical care and auto repairs. This drives up the cost of claims, which insurers often pass on to consumers through increased premiums.
Interest rates also play a crucial role. Insurers invest the premiums they collect. Low interest rates decrease their investment income, potentially putting upward pressure on premiums to compensate. Conversely, higher interest rates can alleviate some of this pressure.
The Impact of Catastrophic Loss Events and Reinsurance
The insurance industry is vulnerable to catastrophic events like natural disasters. A hurricane, for example, can result in a surge of claims, straining insurers' resources. These events often lead to premium increases, not only for those directly affected but for policyholders across the board.
Reinsurance, essentially insurance for insurance companies, also impacts your premium. When reinsurance costs rise, insurers often adjust their pricing, leading to higher premiums for consumers. This complex interplay of factors can make predicting future premium costs challenging.
Emerging Risks and Their Influence on Pricing Models
The insurance industry constantly evolves, facing new and complex risks. Climate change, with its increasing frequency and severity of weather-related events, poses a major challenge. This has led regulators to push for more transparency in how insurers account for these risks, ultimately influencing premiums. Global total real premium growth is forecasted at 2.6% on average for 2025, with life insurance premiums alone expected to reach approximately USD 4.8 trillion. Find more detailed statistics here.
Beyond climate change, cyber threats are another emerging risk. As businesses become increasingly reliant on technology, the potential financial impact of cyberattacks grows. This translates into higher premiums for cyber insurance and may indirectly affect premiums in other areas as insurers adapt.
Social inflation and litigation trends also impact premiums. Increasing jury awards and legal costs contribute to higher claims expenses, which can drive up premiums for policies like liability insurance. Understanding the different types of insurance helps determine premiums, as discussed in this guide to Veteran Life Insurance Options.
Navigating the Shifting Landscape of Insurance Premiums
The factors affecting insurance premiums are complex and interconnected. It’s crucial to view your insurance costs within a broader economic and industry context. By understanding these forces, you can make informed decisions about your coverage and better anticipate future premium changes. This knowledge empowers you to negotiate effectively and find the right balance between cost and protection in a changing risk environment.
Premium Reduction Tactics That Actually Work

Beyond the typical advice, several effective strategies exist to lower your insurance premium—the regular payment you make for coverage—without sacrificing needed protection. These tactics, gathered from insurance professionals and consumer advocates, can significantly impact your yearly insurance costs.
Strategic Deductible Adjustments
One of the most effective ways to lower your premium is by adjusting your deductible. This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. A higher deductible often results in a lower premium.
However, this decision requires careful thought. You must be sure you can comfortably afford the higher deductible if you need to file a claim.
For example, raising your auto insurance deductible from $500 to $1,000 could significantly lower your premium. However, you'll need $1,000 readily available if you're in an accident. This strategy involves balancing potential savings with your financial preparedness.
Uncovering Hidden Discounts
Many insurance companies offer various discounts that policyholders may not be aware of. These might include discounts for safe driving, bundling multiple policies, or installing safety features in your home.
Actively ask about potential discounts to maximize your savings. Some discounts, like those for bundling multiple policies, might seem attractive but aren't always the best deal. Carefully evaluate if bundling truly saves you money compared to maintaining separate policies.
Premium Reduction at Different Life Stages
Your stage of life also presents opportunities for premium adjustments. Young drivers, for instance, usually pay higher premiums. However, maintaining a clean driving record and good grades can often unlock discounts.
As you get older and gain more driving experience, your premiums might naturally decrease. Read also: Unlock Savings: 10 Proven Strategies To Lower Your Life Insurance Costs.
Smart Cost-Cutting vs. Dangerous Coverage Gaps
While saving on premiums is important, avoid reducing coverage to the point of vulnerability. Drastically reducing coverage might save money initially but could lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses if a significant claim arises.
Always prioritize adequate coverage that meets your needs and risk tolerance. This means evaluating your coverage needs and avoiding unnecessary add-ons. Do you really need that extra rider? Could slightly lower coverage limits work without substantially increasing your risk? These questions can help refine your coverage and save on your premium.
By using these premium reduction tactics, you can strengthen your negotiating position with insurers and potentially save significantly on your insurance costs. With this knowledge, you can navigate insurance pricing and secure the best rates without compromising necessary coverage.
Mastering Premium Payments for Maximum Benefit
Your choice of payment options has a significant impact on your insurance costs. This section explores the financial implications of different premium payment options and timing decisions. Understanding these choices is crucial for maximizing the value of your insurance.
Payment Frequency: Monthly vs. Annual Payments
Most insurance companies offer various premium payment frequencies, the most common being monthly and annual payments. While monthly payments offer greater budget flexibility, they often lead to a higher overall cost than annual payments. This is because insurers often add administrative fees or interest charges for the convenience of installment payments.
For example, paying your car insurance premium monthly could add a 5-10% surcharge compared to a single annual payment. Over time, this small percentage can accumulate to a substantial amount. Opting for an annual payment, when financially feasible, can result in significant long-term savings.
Payment Methods and Their Implications
Your chosen payment method can also influence the overall cost. Some insurers provide discounts for automated payments or Electronic Funds Transfers (EFTs), eliminating processing fees associated with manual payments. Paying by check or credit card might incur extra charges, increasing your total expense. Understanding these potential fees is essential when comparing insurance providers and payment options.
Timing Your Payments Strategically
Beyond frequency and method, the timing of your premium payment can also offer advantages. Some insurers offer discounts for paying in full before the due date, rewarding proactive payment management. Synchronizing your payments with specific billing cycles can also allow you to take advantage of potential grace periods and avoid late payment fees.
For further strategies, explore resources like this article on how to lower insurance premiums. Such resources can provide valuable insights and practical tips for managing insurance costs.
Consequences of Missed or Late Payments
What happens if you miss a payment? Most insurance policies include a grace period, usually 10-30 days, during which coverage remains active. However, failing to pay within this grace period can lead to policy cancellation. This leaves you without essential financial protection and could impact your future insurability.
Reinstatement of a lapsed policy is often possible but typically involves additional fees and paperwork. Furthermore, a lapse in coverage could result in higher premiums upon reapplication, as insurers often view those with missed payment history as higher risk. Consistent, on-time premium payments are vital for maintaining both your coverage and long-term financial well-being.
Optimizing Your Premium Payment Strategy
Optimizing your insurance premium payment strategy requires careful consideration of your budget, available payment options, and long-term financial goals. While monthly payments offer short-term budgetary ease, annual payments generally result in lower overall costs. Selecting the appropriate payment method and timing payments strategically can maximize potential discounts and minimize fees. Avoiding late or missed payments is paramount to preventing policy lapses and maintaining affordable insurance coverage. Understanding these factors allows you to manage insurance payments effectively, minimizing costs and ensuring continuous financial protection.
Comments are closed.