Navigating the Self-Employed Health Insurance Landscape

Finding the right health insurance as a self-employed individual can be a daunting task. Unlike those with employer-provided coverage, you are responsible for every step of the process, from researching plans to paying the full premium cost. This requires a thorough understanding of self-employed health insurance, a process that goes beyond simply selecting a plan. It involves developing a strategy that protects both your health and your finances.
Understanding Self-Employment and Insurance Eligibility
One of the first things to do is determine your eligibility. Being "self-employed" in the insurance world isn't limited to established businesses. It covers a wide range of situations, from freelancers with side gigs to independent contractors and small business owners. Even if you're just starting, it’s important to understand your options early on. This proactive approach sets you up for success, both personally and professionally.
The Challenges of the Self-Employed Insurance Marketplace
The marketplace presents specific challenges for independent workers. Generic insurance advice often misses the mark because it doesn't address the unique needs of those without employer subsidies. A primary concern is the rising cost of premiums, which can significantly strain your budget. In the United States, this is especially relevant. As of 2024, annual premiums for single coverage averaged $8,951, a 6% rise from the previous year. Family plans averaged $25,572, a 7% increase. Find more detailed statistics here.
These increasing costs, combined with average deductibles of $1,787, create a significant financial burden for the self-employed. This challenge is underscored by the fact that 62% of employees consider employer-sponsored insurance essential for financial security, highlighting the vulnerability of those without this support.
How Successful Freelancers Approach Coverage
Smart self-employed individuals understand the importance of a personalized approach to health insurance. They frequently explore options beyond traditional plans, including professional association group plans, health sharing ministries, and high-deductible health plans paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). These alternatives may offer cost savings and increased flexibility. You might be interested in: How to Assess Your Needs and Find the Right Provider. Choosing the right coverage isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. It's a process that requires careful consideration of your individual health needs, the stage of your business, and your long-term financial goals.
Breaking Down Your Coverage Options That Actually Work
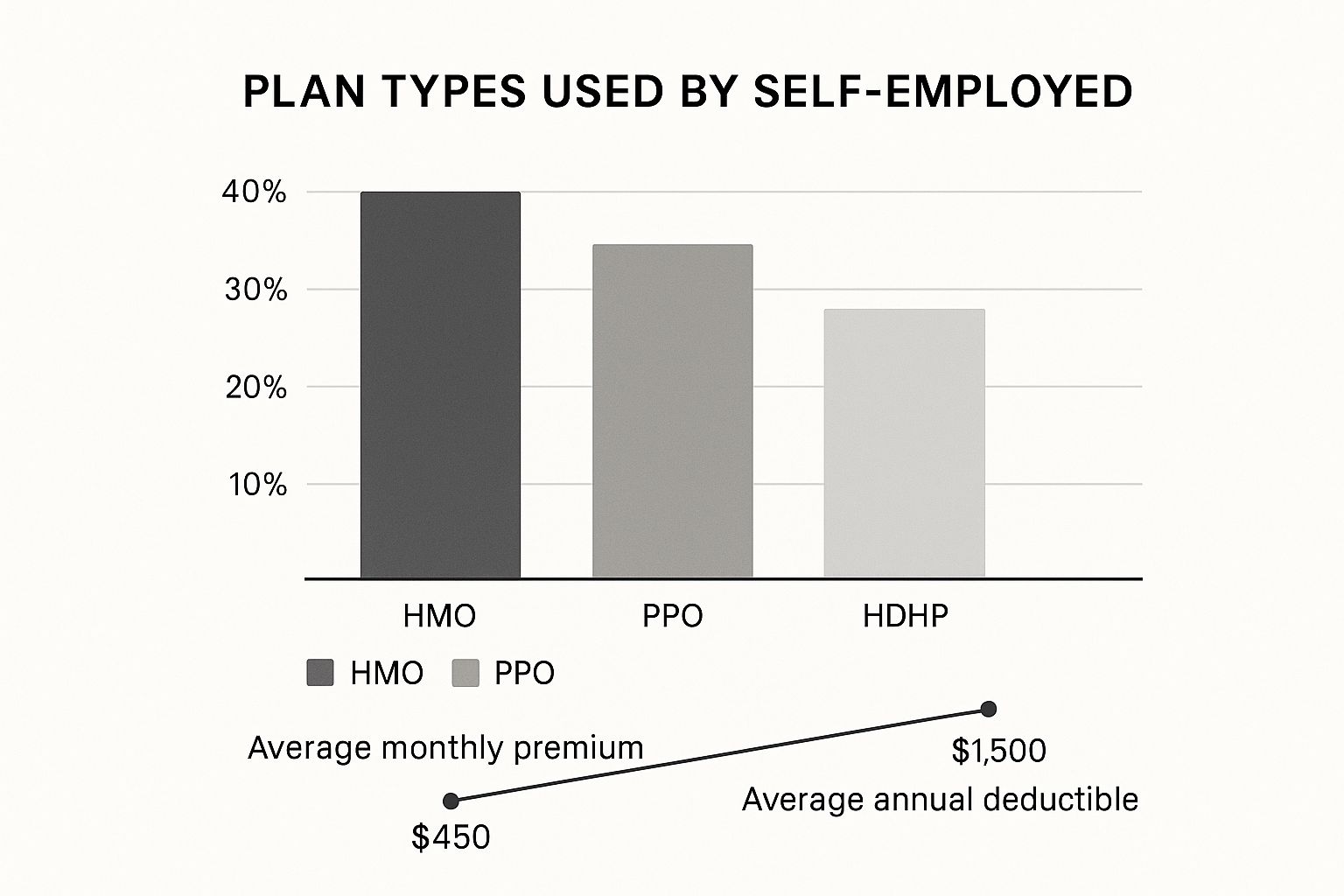
The infographic above illustrates the breakdown of health insurance plan types chosen by self-employed individuals: HMOs, PPOs, and HDHPs. It also shows average monthly premiums and annual deductibles. HMO plans are the most popular, followed by PPOs, with HDHPs representing a smaller, yet significant, segment. This data reflects the balancing act self-employed individuals face when choosing a plan – weighing cost against coverage.
Exploring The Marketplace: Finding A Plan That Fits
The Health Insurance Marketplace is a common resource for finding self-employed health insurance. Marketplaces offer a variety of plans, ranging from bronze to platinum, allowing you to customize coverage based on your needs and budget. For example, if you expect frequent doctor visits, a plan with a lower deductible might be better. However, lower deductibles often mean higher monthly premiums.
Finding the right balance is crucial.
The Power Of Association: Group Plans
Many professional and trade associations offer group health insurance plans to members. These plans can offer significant advantages, such as lower premiums and enhanced benefits, due to the collective bargaining power of the group. Some group plans include features not typically found in individual marketplace plans. This makes them a compelling option for self-employed individuals looking for comprehensive coverage.
Health Sharing Ministries: An Alternative Approach
Health Sharing Ministries (HSMs) provide an alternative to traditional health insurance. Members contribute monthly "shares," which are then used to cover eligible medical expenses within the community. It's important to note that HSMs are not insurance and don't guarantee coverage in the same way traditional insurance does. Thorough research is vital before choosing an HSM.
HdHPs And HSAs: A Strategic Combination
High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) paired with health savings accounts (HSAs) have become a popular strategy. HDHPs typically have lower premiums but higher deductibles. HSAs allow you to save pre-tax dollars to cover those deductibles and other eligible medical expenses. You can use HSA funds for prescriptions, doctor visits, and even certain over-the-counter medications.
This combination offers both short-term premium savings and long-term tax benefits.
To help you further evaluate your options, the following table summarizes the key features of each type of health insurance:
Comparison of Self Employed Health Insurance Options
This table compares the main health insurance options available to self-employed individuals across key factors including costs, coverage quality, eligibility requirements, and benefits/limitations.
| Insurance Type | Average Monthly Premium | Typical Deductible | Key Benefits | Limitations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | $400 – $600 | $2,000 – $5,000 | Lower premiums, co-pays, wide network | Restricted to network providers, referrals required for specialists | Individuals seeking lower costs and predictable expenses |
| PPO | $500 – $800 | $3,000 – $7,000 | Greater flexibility in choosing providers, no referrals needed | Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs | Individuals who want more provider choices and flexibility |
| HDHP | $300 – $500 | $5,000 – $10,000 | Lowest premiums, HSA eligible | High deductible, more financial risk | Healthy individuals comfortable with higher out-of-pocket costs |
| Group Plan (through association) | Varies | Varies | Potential for lower premiums and better benefits than individual plans | May have specific eligibility requirements based on association membership | Individuals belonging to a professional or trade association |
| Health Sharing Ministry | Varies | Varies | Shared costs within a community, often lower monthly contributions | Not technically insurance, coverage not guaranteed, may have restrictions based on shared beliefs | Individuals seeking a faith-based or community-focused approach |
This table provides a general overview, and actual costs and benefits can vary widely. Be sure to compare specific plans carefully.
Evaluating Your Options
Choosing the right self-employed health insurance requires careful consideration. Factors like your health, expected medical needs, and budget play a significant role. Your business stage is also important. A newer business with limited income might prioritize affordability, while a more established business may seek more comprehensive coverage. Understanding your individual profile will help you make informed decisions.
Cost-Taming Techniques Top Freelancers Actually Use

Making self-employed health insurance affordable requires a proactive approach. This goes beyond simply selecting a plan. It means actively looking for ways to reduce costs. Successful freelancers use several strategies to effectively manage their healthcare expenses.
Leveraging HSAs and FSAs
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) are valuable tools. HSAs, combined with high-deductible health plans, allow pre-tax contributions. These contributions cover qualified medical expenses. This offers immediate savings and long-term tax advantages. FSAs also allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars for healthcare costs, reducing your taxable income. Understanding these accounts can significantly impact your finances.
Maximizing Premium Tax Credits
Premium tax credits can significantly lower monthly insurance premiums. These credits are available through the Health Insurance Marketplace. They are based on your income. Understanding the subsidy thresholds is crucial for maximizing eligibility. Stay informed about income limits. Know how income changes affect your credit amount. This knowledge helps you plan strategically.
Income Management for Optimal Eligibility
Managing income strategically can also influence eligibility for premium tax credits. Carefully timing deductions and income streams can help you stay within subsidy limits. This requires planning. It involves understanding how income affects your tax liability.
Negotiating Cash Rates With Providers
Many freelancers negotiate cash rates directly with healthcare providers. This can often result in lower costs than using insurance. This is especially true for routine visits or procedures. Building relationships with providers can help with these negotiations.
Exploring Cost-Sharing Programs
Several cost-sharing programs can help reduce out-of-pocket expenses. These programs are often overlooked. They are not always widely advertised. Actively researching and inquiring about these programs can uncover valuable savings.
Focusing on Preventive Care
Prioritizing preventive care is a key long-term cost management strategy. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of developing costly medical conditions. This proactive approach saves money. It also protects your ability to work. Globally, rising healthcare costs heavily influence the self-employed health insurance market. Worldwide expenses are projected to rise by 10.2% in 2025, up from 9.3% in 2024. This directly affects self-employed individuals, who often bear the full cost of coverage. Explore this topic further.
By implementing these cost-taming techniques, self-employed individuals can navigate the health insurance landscape effectively. They can ensure adequate coverage without compromising financial well-being. This proactive mindset is crucial for long-term success and peace of mind.
Unlocking The Tax Advantages Most Freelancers Miss
As a self-employed individual, managing health insurance can feel like a burden. However, understanding the tax advantages available can transform this into an opportunity for significant savings. There's more to it than simply deducting premiums; a whole range of tax benefits can positively impact your bottom line.
Maximizing Deductions: Strategies And Structures
Smart freelancers often structure their businesses to optimize tax benefits related to self-employed health insurance. This involves diligent record-keeping and a solid understanding of eligible deductions. For instance, you can deduct 100% of your health insurance premiums, including those for your spouse and dependents. Understanding your tax obligations is crucial; see this article about managing LLC Self Employment Taxes Strategies.
Also, consider options like Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). HSAs offer triple tax advantages:
- Contributions are tax-deductible
- Growth is tax-free
- Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free
Navigating Audits: Documentation And Timing
Protecting yourself during tax audits is essential. A well-organized documentation system is key, including records of all health insurance premiums paid, medical expense receipts, and any HSA-related documents.
Timing matters too. Understanding deadlines for contributions and deductions can maximize your tax benefits. For example, contributing to your HSA before the tax deadline can significantly reduce your taxable income for the year.
To help illustrate the tax benefits available, let's take a look at the table below:
Self Employed Health Insurance Tax Benefits
This table outlines the key tax advantages available to self-employed individuals for health insurance expenses, including eligibility criteria and potential savings.
| Tax Benefit Type | Potential Savings | Eligibility Requirements | How to Claim | Documentation Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction | Up to 100% of premiums paid | Must be self-employed and not eligible for employer-sponsored health insurance | Form 1040, Schedule C | Proof of premiums paid |
| HSA Deduction | Varies based on contributions and tax bracket | Must have a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | Form 8889 | Form 5498-SA |
| HSA Tax-Free Growth | Varies based on investment performance | Must have an HSA | N/A | N/A |
| HSA Tax-Free Withdrawals | Varies based on qualified medical expenses | Must have an HSA and use funds for qualified medical expenses | N/A | Receipts for qualified medical expenses |
This table summarizes the main tax advantages for self-employed individuals regarding health insurance. By understanding these benefits and how to claim them, you can potentially save a substantial amount on your taxes.
Staying Informed: Thresholds, Limits, And Changes
Tax laws are constantly changing. Staying informed about updates, deduction thresholds, and HSA contribution limits is vital for optimizing your tax strategy. Recent changes might affect your eligibility for certain deductions or credits. Knowing these details can significantly impact your overall tax burden. This is particularly important for self-employed individuals, who manage their own taxes. You might be interested in: How to Master the Tax Advantages of Life Insurance. Staying updated allows you to adapt and maximize potential savings.
Real-World Examples: Savings In Action
Savvy self-employed professionals use these strategies to save thousands on their taxes. One example is a freelancer who structured their business as a sole proprietorship and maximized health insurance premium deductions, saving over $3,000 annually. Another example is a consultant who diligently used an HSA, accumulating tax-free savings for future medical expenses. By combining strategic planning with a deep understanding of tax benefits, these individuals transformed their health insurance from an expense into an asset. These real-world successes highlight the power of leveraging the tax advantages available. By actively engaging with these strategies, you can reduce your tax burden and free up resources.
Future-Proofing Your Coverage in a Changing Landscape

The self-employed health insurance market is in constant flux. Staying up-to-date on emerging trends and adapting your long-term coverage strategy is essential for protecting your health and financial well-being. Forward-thinking independent contractors are already capitalizing on these shifts.
Technology's Impact on Insurance Models
Technology is transforming how we access and manage healthcare. New platforms designed specifically for freelancers are emerging. These platforms frequently offer simplified application processes, personalized plan recommendations, and digital tools for managing claims and expenses.
Some platforms use AI to match individuals with optimal plans based on their health and financial profiles. This personalized approach can save both time and money.
International Approaches to Watch
Examining international models offers valuable insights into the future of self-employed health insurance. Some countries offer portable insurance plans that stay with individuals regardless of their employment status. Others have established national health insurance systems covering all citizens, including the self-employed. These examples showcase diverse approaches to healthcare access for independent workers.
Digital Health Innovations and Value
Digital health innovations are also having a major impact. Telemedicine, virtual care, and wearable health trackers are growing in popularity among the self-employed. These tools provide convenient access to healthcare services and may potentially lower costs. This is especially helpful for remote workers or those with limited time for traditional doctor visits.
Many freelancers file taxes online. Understanding the impact of tax benefits on your healthcare coverage strategy is important. For a helpful resource, check out this guide on filing business taxes online.
The Evolving Landscape of Self-Employed Healthcare Costs
Health insurance trends reveal a complicated situation for self-employed individuals, particularly in major markets like the U.S., Europe, and Asia. Statistical forecasts predict substantial increases in medical trend rates globally, directly impacting insurance premiums.
In high-income countries like the United States, projected annual premium growth ranges from 6-8% due to factors like advancements in medical technology, rising pharmaceutical costs, and increased healthcare utilization. For self-employed individuals, this means higher out-of-pocket expenses, especially as they often purchase individual market plans, which typically have higher premiums and deductibles compared to employer-sponsored plans. Learn more about global medical trends.
These escalating costs often lead self-employed individuals to explore options like HSAs (Health Savings Accounts), high-deductible health plans, or government subsidies. Many countries are also developing insurance products specifically designed for the self-employed, recognizing their growing presence in the workforce.
Shifting Demographics and Opportunities
Workforce demographics are changing. The number of self-employed individuals continues to rise. This creates both challenges and opportunities. Increased demand for customized insurance solutions for freelancers may spur market innovation, potentially leading to more flexible and affordable coverage options.
Policy Developments and Future Coverage
Policy changes can significantly affect self-employed health insurance options. Staying informed about legislative developments at both the state and national levels is vital for long-term planning. These changes could include new regulations, subsidies, or tax benefits. See also: Tips to Choose the Right Plan.
By staying aware of these changes, you can proactively adjust your strategy to maintain adequate and affordable coverage, ensuring both your health and business thrive in the dynamic self-employment landscape.
Crafting Your Personalized Self-Employed Insurance Blueprint
Now that we’ve explored the world of self-employed health insurance, it’s time to create a personalized plan. This involves a step-by-step approach designed for your specific needs and circumstances, much like how successful freelancers build their businesses.
Assessing Your Needs and Risk Tolerance
First, honestly assess your health status and anticipated medical needs. Are you generally healthy, or do you have pre-existing conditions that require regular care? Consider your family's needs as well, if you have dependents. This evaluation forms the foundation of your insurance strategy.
Next, evaluate your risk tolerance. Are you comfortable with a high-deductible plan in exchange for lower premiums, or do you prefer the predictability of higher premiums and lower out-of-pocket costs? Finding a balance between cost and coverage is essential.
Building Your Coverage Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
Think of this process as building blocks for your health insurance coverage. Each step builds upon the previous one, ultimately creating a solid, personalized plan:
- Step 1: Define Your Budget: Determine how much you can realistically afford to spend on health insurance premiums and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
- Step 2: Explore Your Options: Research various options, including marketplace plans, association plans, HMOs, and HDHPs with HSAs.
- Step 3: Compare Plans: Don't just focus on premiums. Compare deductibles, co-pays, out-of-pocket maximums, and covered services.
- Step 4: Consider Tax Advantages: Explore tax benefits associated with different plans, such as the self-employed health insurance deduction and HSA contributions.
- Step 5: Enroll and Implement: Choose the plan that aligns with your needs, budget, and risk tolerance, then complete the enrollment process.
Combining Insurance Components for Comprehensive Coverage
Think of your insurance coverage as a safety net. A single plan may not cover all your needs. For example, you might combine a high-deductible plan with an HSA for routine care and critical illness insurance for catastrophic events.
Additionally, consider supplemental plans like accident insurance or disability insurance to fill any potential gaps in your core coverage. This layered approach creates a more complete safety net.
Real-World Examples: Personalized Strategies in Action
One freelancer, after carefully assessing their needs, chose a high-deductible health plan paired with an HSA, maximizing their tax savings while ensuring coverage for potential major medical expenses. Another opted for an association plan offering lower premiums and broader coverage through group leverage. These examples highlight the value of a personalized approach.
Contingency Planning: Protecting Your Health and Business
What if your health situation changes, or your business income fluctuates? Having a contingency plan is essential. This plan could involve adjusting your coverage level or exploring alternative options like short-term health insurance during periods of lower income. You might also consider increasing HSA contributions during more prosperous times. Being adaptable ensures continuous coverage, even during changes in circumstances.
Actionable Tools and Implementation Timelines
Moving from planning to action requires practical tools. Develop a timeline for reviewing your coverage annually or when significant life changes occur. Use online resources and worksheets to track your expenses and stay organized. This structured approach ensures you’re always prepared.
By following these steps, you can create a self-employed health insurance plan tailored to your individual needs, developing a strategy that protects both your health and financial future. This allows you to focus on what you do best – running your business.
Comments are closed.