The Science Behind Your Premium: Insurance Math Unveiled

Calculating your car insurance premium isn't a random process; it's a complex calculation based on statistical analysis and risk assessment. This process has changed dramatically over time, moving from simple manual calculations to complex algorithms that can handle massive amounts of data. This allows insurers to predict risk more accurately, leading to more personalized premiums.
From Manual to Algorithmic: The Evolution of Premium Calculation
Initially, insurers used simpler methods, relying on basic information like your age, driving record, and vehicle type. These broad categories often led to less precise risk assessments. For example, two 25-year-old drivers with the same car could face different premiums simply due to their zip codes.
Today's models go far beyond these basic factors. Insurers now utilize advanced statistical methods, including Generalized Linear Modeling (GLM), to analyze the probability and cost of potential claims. These models consider a wide array of variables, from your credit history to the safety features of your car.
How GLM Works
Car insurance premiums are determined using several factors, including the likelihood and cost of claims. GLM models claim frequency and severity. For instance, in France, the average annual car premium was around €400 in 2016, reflecting a relatively stable trend. Find more detailed statistics here While GLM is a valuable tool, the inherent simplicity of basic premium calculation methods can limit its broader applicability. Factors such as vehicle type, driving history, and location significantly impact premiums. Drivers in urban areas often pay higher rates due to increased risks of accidents and theft. This detailed analysis allows for a more precise understanding of individual risk, leading to premiums that better reflect individual circumstances.
The Balancing Act: Profitability vs. Competitive Pricing
Insurers must strike a balance between remaining profitable and offering competitive prices. They use sophisticated algorithms to analyze vast datasets, identifying patterns and correlations that predict the likelihood of future claims. This predictive modeling is crucial for setting premiums that allow for both competitive pricing and a sustainable business model. This constant evaluation considers market trends, competitor pricing, and the overall economic climate.
The Data Puzzle: How Your Information Becomes a Premium
Insurers piece together a comprehensive risk profile using numerous data points. This includes information you provide directly, such as your address and driving history, as well as data gathered from third-party sources. This data is then input into complex algorithms that assess your risk level and calculate your premium. The algorithms consider how each factor interacts with others to create a personalized premium that reflects your individual risk profile. This complex process allows insurers to accurately assess your likelihood of filing a claim and offer appropriate coverage at a fair price.
The Premium Puzzle: Key Factors That Shape Your Rates
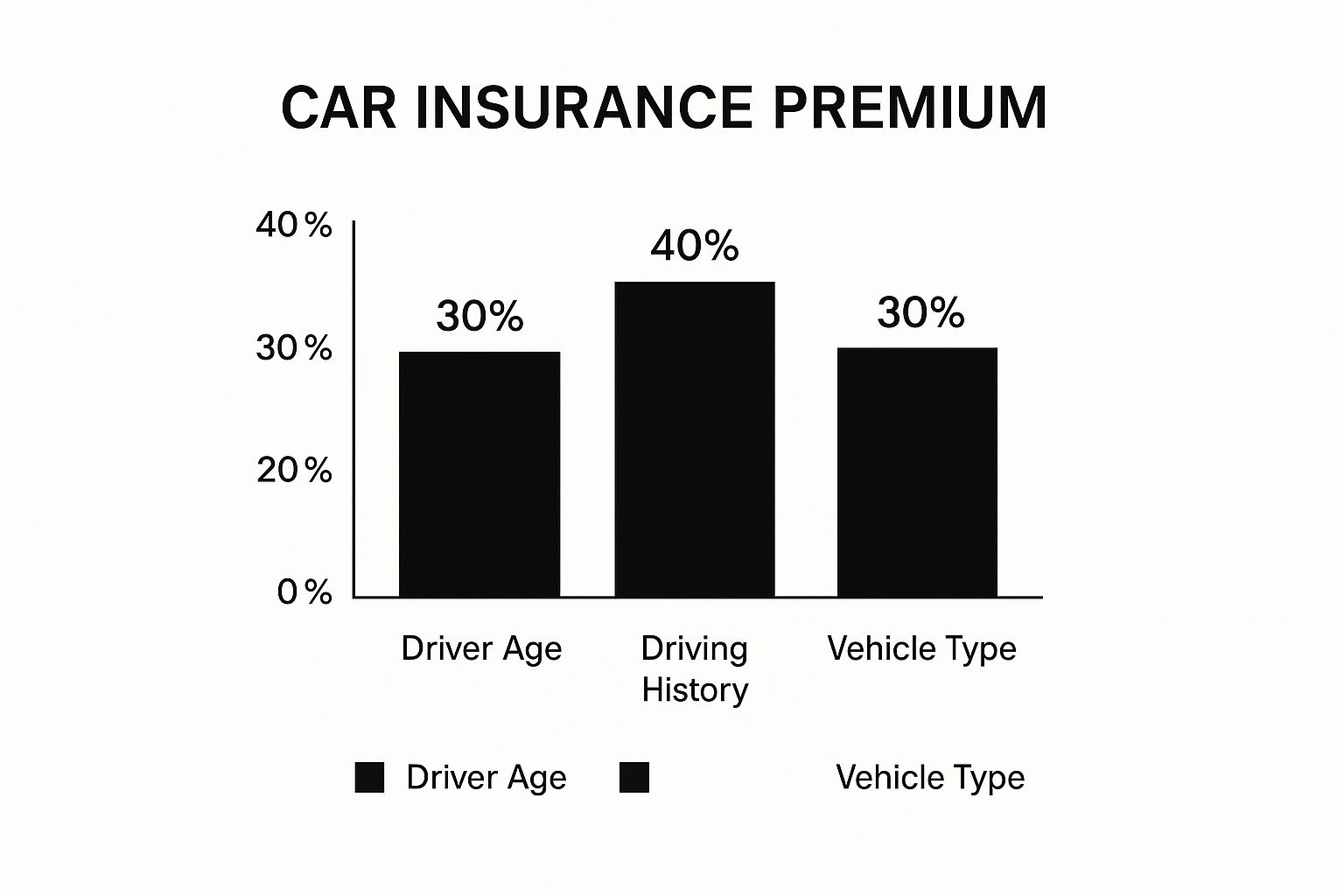
This infographic clearly shows how three major elements – driver age, driving history, and vehicle type – affect your car insurance premium. Driving history has the biggest impact, emphasizing the importance of a clean driving record.
Your car insurance premium isn't a random number. It's calculated using a complex formula based on several interconnected factors that help insurers assess your risk profile. Let's break down these key components.
Driver Demographics and Their Impact
Several personal details, such as your age, marital status, and gender, can influence your insurance rates. Younger, less experienced drivers statistically have a higher risk of accidents, resulting in higher premiums. A teenager, for example, will likely pay significantly more than a middle-aged driver with a spotless record.
Some insurers consider married couples as more responsible and stable, potentially leading to lower rates. However, this can vary between different insurance providers.
Let's explore this further in the table below:
Impact of Driver Demographics on Insurance Premiums
This table shows how different driver characteristics typically affect insurance premium calculations.
| Driver Factor | Impact on Premium | Risk Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Younger Age (especially teenagers) | Significantly Higher | Statistically higher risk of accidents due to inexperience. |
| Older Age (Seniors) | Can be Higher or Lower | Depending on health and cognitive abilities; potential for slower reflexes. |
| Marital Status (Married) | Potentially Lower | Often seen as more responsible and stable by insurers. |
| Gender | Varies | Statistical differences in driving habits can sometimes influence premiums. |
This table demonstrates how age and marital status are often significant factors in determining insurance premiums, reflecting perceived risk levels. Other demographics can also play a role depending on the insurer's specific calculations.
The Weight of Your Driving Record
Your driving history is a major piece of the premium puzzle. Accidents and traffic violations indicate higher risk, resulting in increased premiums. The severity and recency of these incidents are also important.
A recent speeding ticket will have a greater impact than one from years ago. The number of claims filed also contributes to your premium calculations.
Location, Location, Location: Where You Live Matters
Your location significantly influences your insurance costs. Urban areas typically have higher rates than rural locations due to increased risks of accidents, theft, and vandalism. Explore this topic further.
This is because insurers adjust their formulas to reflect the varying risks associated with different regions. Even your ZIP code can affect your premium.
Your Vehicle's Profile: Make, Model, and More
The car you drive also plays a role in your premium calculation. Insurers consider factors like safety features, repair costs, and the likelihood of theft. A sports car, for instance, is often more expensive to insure than a family sedan due to higher repair costs and greater theft appeal.
Similar to how car insurance protects your vehicle, you might consider insuring items in storage. You might also be interested in learning how to master your home insurance costs. Insurance pricing considers various aspects of risk, including driver demographics and vehicle characteristics, to arrive at the final premium.
Crunching The Numbers: How Actuaries Calculate Your Cost

Ever wonder how your car insurance premium is calculated? It's more than just a simple dollar figure. Behind the scenes, actuaries use complex mathematical formulas to determine your personalized price. They analyze vast amounts of data, taking into account your driving profile and other key factors to predict risk and set appropriate premiums. Let's delve into this intricate process.
Risk Pooling and the Law of Large Numbers
Insurance companies rely on the principle of risk pooling. This involves collecting premiums from a large group of drivers, creating a shared fund to cover potential claims. The law of large numbers is central to this concept. As the number of insured drivers increases, the actual claims filed tend to align more closely with predicted probabilities. This allows insurers to forecast and manage their financial obligations with greater accuracy. For instance, while a small group of drivers may have unpredictable claim patterns, a larger group provides a more stable and predictable basis for forecasting.
Claim Frequency and Economic Factors
A crucial element in premium calculation is claim frequency, often expressed as the rate per 100 insured vehicle years. This metric helps actuaries understand the likelihood of claims, a fundamental aspect of premium determination. Global economic conditions also play a significant role. Factors like inflation and rising repair costs can drive up insurance rates. For example, recent data revealed an 11.3% increase in car insurance rates in the year leading up to December 2024. Discover more insights about auto insurance statistics.
Balancing Mathematical Models and Data Collection
Insurers utilize sophisticated mathematical models to analyze risk and calculate premiums. These models require a balance of accuracy and practicality, considering the complexity of the data and available computational resources. A wide range of data points is collected, including some that may seem unrelated to driving. Understanding risk is paramount, and for businesses, understanding risk management within their operations is just as critical. Consider exploring resources on business insurance for more information. This collected information helps refine risk profiles and tailor premiums to individual drivers, leading to more accurate claim predictions. For example, credit history can sometimes correlate with driving behavior and claims frequency, ultimately influencing premiums.
To illustrate the various components that contribute to a car insurance premium, let's examine the following table:
Car Insurance Premium Calculation Components
This table provides a breakdown of the mathematical elements that make up a typical car insurance premium calculation.
| Calculation Component | Definition | Weight in Final Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Driving History | Record of accidents, violations, and claims | High |
| Vehicle Type | Make, model, and year of the car | Medium |
| Location | Where the car is primarily driven and stored | Medium |
| Credit History | Individual's credit score and history | Low to Medium |
| Age and Gender | Demographic factors | Low |
| Coverage Level | Amount of insurance chosen | High |
| Deductible | Amount paid out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in | Medium |
As shown in the table, factors like driving history and coverage levels carry significant weight, while demographics and credit history play a lesser, though still important role.
Determining a Fair Price
The ultimate goal of actuarial science in car insurance is to establish a fair price that accurately reflects individual risk. This involves assigning higher premiums to higher-risk drivers and offering discounts to lower-risk drivers. Various factors contribute to this assessment, including driving history, vehicle type, and location. This meticulous analysis aims to distribute the cost of insurance equitably across the insured population, ensuring that each driver pays a premium commensurate with their risk profile.
Digital Profiling: Modern Risk Assessment Techniques

Car insurance companies are increasingly using digital technologies to assess driver risk. This goes beyond simply checking your driving record. They're building detailed digital profiles to understand your potential for future claims. This means how car insurance is calculated is becoming more complex and personalized.
Telematics: Tracking Your Driving Habits
One key technology used in digital profiling is telematics. This involves using devices to monitor your actual driving behavior. These devices, often plugged into your car's diagnostic port or accessed through smartphone apps, collect data on your speed, braking habits, acceleration, and mileage.
For example, frequent hard braking or rapid acceleration could be flagged as high-risk behavior, potentially increasing your premiums. This data provides a more nuanced picture of your driving habits than a simple driving record check.
AI and Predictive Analytics: Forecasting Future Claims
Insurers are also using Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms, along with predictive analytics, to forecast the likelihood of a claim. These AI algorithms analyze large datasets of driver information, searching for patterns and correlations that may indicate risk.
This means factors beyond your control, such as your socioeconomic background, might indirectly influence your premium through these predictive models. This use of AI raises important ethical questions about fairness and transparency in how insurance is priced.
From Demographics to Personalized Risk
This shift toward digital profiling represents a significant move away from broad demographic categories. Insurers are transitioning to hyper-personalized risk assessments, tailoring premiums more precisely to individual driving behavior and predicted risk.
However, this personalized approach means insurers have access to a considerable amount of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security. Understanding how these new assessment models work is crucial for drivers to manage their insurance costs effectively.
High-Risk Behaviors in the Digital Age
Modern telematics systems can flag a variety of driving behaviors as high-risk. These behaviors include speeding, tailgating, frequent lane changes, and driving late at night.
However, simply avoiding these flagged behaviors doesn't guarantee a lower premium. AI algorithms consider a multitude of factors in their complex risk calculations, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact impact of any single behavior.
Positioning Yourself Favorably: Tips for the Modern Driver
So, how can you position yourself favorably in this new era of digital profiling? One strategy is to opt into telematics programs offered by some insurers. These programs allow you to actively demonstrate safe driving habits, potentially earning discounts.
Additionally, maintaining a clean driving record and choosing a car with robust safety features can positively influence your risk profile. Staying informed about how insurers are using these technologies and understanding how car insurance is calculated can empower you to find the best coverage at the most competitive price.
Location Matters: Why Your Address Drives Your Rate
Your ZIP code plays a significant role in determining your car insurance premium. It might surprise you to learn that your rate could be hundreds of dollars more than someone living just a few streets over, even with the same car and driving record. This difference stems from the complex formula used to calculate car insurance premiums, which incorporates several location-based factors.
Geographic Factors and Your Premium
Insurers consider a range of geographic factors when setting your rate. These factors include local accident statistics, car theft rates, weather patterns, and even the quality of the local infrastructure. Areas with high accident rates or frequent car thefts are deemed higher risk, leading to increased premiums for drivers in those locations. Similarly, regions prone to severe weather events, such as hailstorms or flooding, also tend to have higher rates.
Real-World Premium Comparisons
The effect of location on car insurance premiums can be substantial. Consider two drivers with identical cars and driving histories. One lives in a busy city center with high traffic congestion and theft, while the other lives in a quiet suburban area. The driver in the city center will almost certainly pay more for insurance simply because of their location.
Regional Regulations and Consumer Protection
Regulations exist in certain areas to protect consumers from specific pricing practices. Such regulations can limit the extent to which insurers can factor location into their premium calculations. However, these regulations differ significantly from region to region, and some areas may offer less consumer protection. It's essential to research the specific regulations in your area to understand their potential impact on your insurance rates. You might also want to read more about how location affects other types of insurance, like: The Surprising Factors That Have the Most Impact on Home Insurance Prices.
High-Risk Zones and Strategic Mitigation
Some areas are designated as high-risk zones due to higher location-based surcharges. These zones typically exhibit a combination of factors, such as high crime, frequent accidents, and subpar road conditions. Even if you reside in a high-risk zone, strategies can help you mitigate premium increases attributed to your location.
Reducing Your Premium Without Relocating
Relocating isn't the only way to lower your insurance costs. Installing anti-theft devices, parking your car in a garage, and completing a defensive driving course can often help reduce your premium, even in high-risk areas. By demonstrating a proactive approach to risk management, you can potentially offset some or all of the location-based surcharges. Choosing a car equipped with advanced safety features can also contribute to lower insurance premiums.
Premium-Cutting Playbook: Proven Strategies That Work
Knowing how car insurance is calculated is the first step. Now, let’s explore how to use that knowledge to reduce your premium. This isn't about basic tips; we're diving into actionable strategies that directly impact how insurers determine your rates.
Discounts That Deliver: Separating the Substantial From the Marginal
Many insurers offer various discounts, but their impact varies significantly. Some offer substantial savings, while others provide only marginal benefits. For example, a multi-policy discount for bundling home and auto insurance with a company like State Farm can significantly lower your overall costs. Similarly, safe driver discounts, earned through consistent accident-free driving, can make a noticeable difference.
However, smaller discounts, like those for paperless billing, offer less impactful savings. Analyzing these offerings and prioritizing the most valuable ones is crucial for maximizing your premium reductions.
Timing Is Everything: Strategic Policy Changes
The timing of your policy changes can significantly influence your premium. Renewing your policy early, before it expires, can sometimes secure a lower rate. Additionally, reassessing your coverage needs annually allows you to make strategic adjustments.
Perhaps you no longer need collision coverage on an older vehicle. Or, a higher deductible might be more suitable for your current financial situation. Strategically timing these adjustments can lead to further savings.
Coverage Modifications: Balancing Value and Protection
Modifying your coverage is another effective way to reduce your premium. Increasing your deductible, the amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage begins, can significantly lower your premium. However, it's essential to choose a deductible you can comfortably afford if an accident occurs.
Dropping certain coverages altogether, such as collision or comprehensive, can also reduce costs. This decision should be made carefully, considering your individual circumstances and the value of your vehicle.
Inside the Insurer's Mind: Psychological Pricing and Negotiation
Insurance pricing isn't solely based on mathematical calculations. Psychological factors can also influence the process. Agents might present quotes strategically to affect your perception of value.
Learning to recognize these tactics and negotiating effectively can help you secure a better deal. For example, demonstrating a willingness to walk away from a quote you consider too high can sometimes prompt a more competitive offer. Learn more in our article about How to master car insurance premium negotiation.
Long-Term Strategies: Reshaping Your Risk Profile
Lowering your premium is an ongoing process. Long-term strategies, implemented consistently, can significantly reshape your risk profile. Maintaining a clean driving record, consistently taking advantage of available discounts, and regularly reviewing your coverage needs are key components of this approach.
This consistent effort demonstrates responsible driving habits and financial awareness—factors that insurers value and often reward. Improving your credit score can also positively influence your rates with some insurers.
Case Studies: Real Drivers, Real Savings
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how drivers successfully reduce their insurance premiums. One driver significantly lowered their rate by increasing their deductible and enrolling in a telematics program that tracked their safe driving habits. Another driver saved money by switching to a usage-based insurance program that charged based on mileage driven.
These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of applying specific strategies. They also highlight the importance of understanding how car insurance is calculated, allowing drivers to identify personalized savings opportunities. You might be interested in: 10 Proven Ways To Slash Your Car Insurance Premiums.
Comments are closed.